
Did you know, 3/10 men and 1/5 women have sleep apnea.1 Learn more about your sleep today, it only takes a few minutes.
Friendly, professional and informative staff that were happy to answer my questions and meet my needs. Much appreciated.
Fast efficient service. I have received excellent service and support from ResMed consultants and sleep coaches. The products I ordered arrived quickly and follow-up from ResMed has been great. Could not recommend more highly. In my opinion, ResMed are streets ahead of their competitors in terms of product quality and service.
My sleep coach has been amazing & encouraging & I feel so much better only after 4 days, so surprised. Everyone I've dealt with at resmed has been so nice & helpful

A premium auto-adjusting obstructive sleep apnea machine with advanced features for your sleeping comfort.
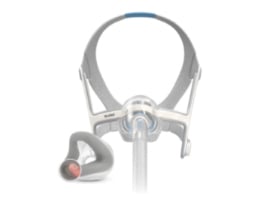
Designed to fit any face shape or size, the AirFit N20 moves comfortably with you through the night.

Small, Smart, Proven - Suitable for use at home or while you’re away. You’ll never have to choose between therapy performance and freedom again.
Educational resources and support to help you and your loved ones sleep better, every night.
Enjoy free shipping Australia wide on all orders.
We’re here to help you get the sleep you deserve.
You can rest assured that we use best-in-class security to process your payments
Chat to our friendly staff at your local ResMed store or authorised dealer.